What is secreted by the highlighted cell – Unveiling the intricacies of cell secretions, this discourse embarks on a journey to explore the diverse molecules released by cells, delving into their functions, mechanisms, and clinical significance.
Cell secretions encompass a vast array of substances, each playing a crucial role in intercellular communication, tissue homeostasis, and immune responses. Understanding the nature of these secreted molecules is paramount to comprehending the intricate workings of biological systems.
Cell Secretions
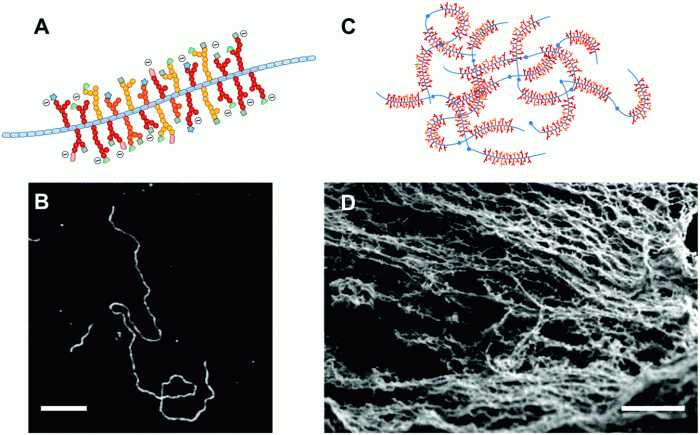
Cell secretions are chemical substances released by cells into the extracellular environment. They play crucial roles in various biological processes, including cell communication, immune response, and tissue homeostasis.
Cell secretions can be classified into three main types based on their composition and function:
- Endocrine secretions:Hormones released into the bloodstream to regulate distant target cells.
- Exocrine secretions:Enzymes, mucus, and other substances released into ducts or cavities for specific functions.
- Autocrine/paracrine secretions:Substances that act on the same cell that secretes them (autocrine) or on nearby cells (paracrine).
Examples of specific cell secretions include:
- Insulin (endocrine): Regulates blood glucose levels.
- Pepsin (exocrine): Digestive enzyme produced by stomach cells.
- Cytokines (autocrine/paracrine): Immune signaling molecules.
Mechanisms of Secretion
Cell secretion occurs through various mechanisms:
Exocytosis
In exocytosis, secretory vesicles containing the secreted substance fuse with the cell membrane and release their contents into the extracellular space.
Endocytosis
Endocytosis is the process of taking substances into the cell from the extracellular environment. It includes phagocytosis (ingestion of large particles) and pinocytosis (ingestion of small particles).
Secretory Vesicles and Golgi Apparatus, What is secreted by the highlighted cell
Secretory vesicles are membrane-bound organelles that store and transport secreted substances. The Golgi apparatus modifies and packages proteins for secretion into secretory vesicles.
Regulation of Secretion
Cell secretion is tightly regulated to ensure appropriate responses to specific stimuli:
Hormones and Neurotransmitters
Hormones and neurotransmitters act as signaling molecules that trigger secretion in target cells.
Feedback Inhibition
Feedback inhibition occurs when the secreted substance itself inhibits its own secretion, preventing excessive release.
Autocrine Signaling
Autocrine signaling involves secreted substances acting on the same cell that released them, providing a means of self-regulation.
Clinical Significance of Cell Secretions
Dysregulated cell secretions can contribute to various diseases:
Cancer
Abnormal secretion of growth factors and other signaling molecules can promote cancer cell proliferation and metastasis.
Immune Disorders
Dysregulated secretion of cytokines and other immune mediators can lead to autoimmune diseases and allergies.
Diagnostic Tests and Interventions
Measurement of cell secretions is used in diagnostic tests for various diseases. Therapeutic interventions targeting cell secretion include hormone replacement therapy and immunomodulators.
Advanced Research and Applications: What Is Secreted By The Highlighted Cell
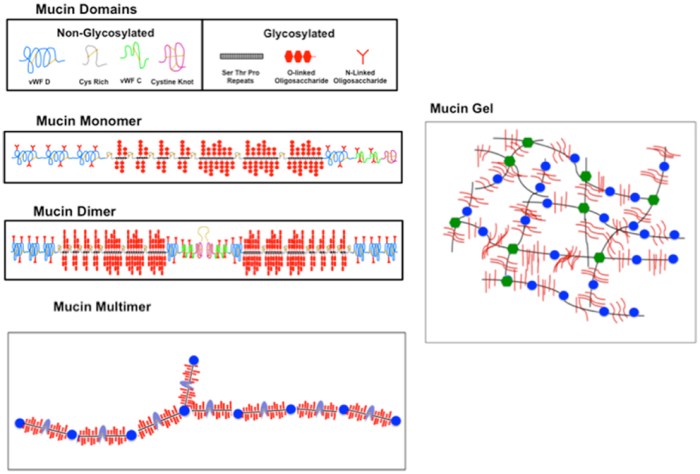
Ongoing research focuses on:
Biotechnology and Medicine
Exploring the potential of cell secretions in drug development, tissue engineering, and regenerative medicine.
Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine
Using cell secretions to promote tissue repair and regeneration.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the primary functions of cell secretions?
Cell secretions serve a multitude of functions, including intercellular communication, nutrient acquisition, waste removal, immune defense, and tissue repair.
How are cell secretions regulated?
Cell secretions are regulated by a complex interplay of factors, including hormones, neurotransmitters, and intracellular signaling molecules. Feedback inhibition and autocrine signaling are key mechanisms involved in maintaining secretion homeostasis.
What is the clinical significance of abnormal cell secretions?
Dysregulated cell secretions can contribute to a range of diseases, such as cancer, immune disorders, and metabolic syndromes. Diagnostic tests and therapeutic interventions targeting cell secretions are essential for managing these conditions.