Hardy weinberg equation pogil answer key – Delve into the fascinating realm of population genetics with the Hardy-Weinberg Equation POGIL Answer Key, a comprehensive guide that unlocks the mysteries of allele and genotype frequencies, equilibrium factors, and the equation’s diverse applications. Prepare to unravel the intricate tapestry of genetic diversity and evolution as we embark on this scientific expedition.
The Hardy-Weinberg Equation, a cornerstone of population genetics, provides a theoretical framework for understanding the distribution of alleles and genotypes within a population. This equation assumes an idealized state of equilibrium, where allele and genotype frequencies remain constant from generation to generation.
However, various factors, such as non-random mating, gene flow, genetic drift, and natural selection, can disrupt this equilibrium, leading to changes in genetic composition.
Hardy-Weinberg Equation
The Hardy-Weinberg equation is a mathematical model that describes the genetic variation in a population under certain assumptions. It provides a baseline for comparing observed genetic frequencies to expected frequencies under the assumption of no evolutionary influences.
Assumptions and Limitations
- No mutations
- No gene flow
- No genetic drift
- Random mating
- No natural selection
Allele and Genotype Frequencies
The Hardy-Weinberg equation can be used to calculate allele and genotype frequencies in a population. Allele frequencies are the proportions of different alleles at a specific gene locus, while genotype frequencies are the proportions of different genotypes in a population.
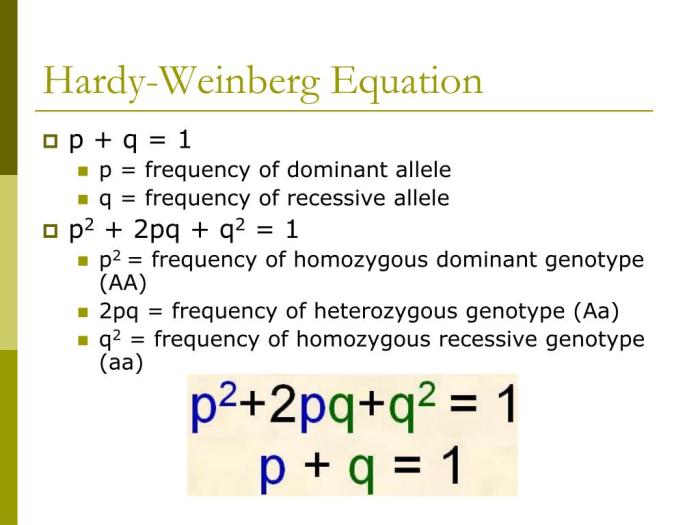
The equation is:
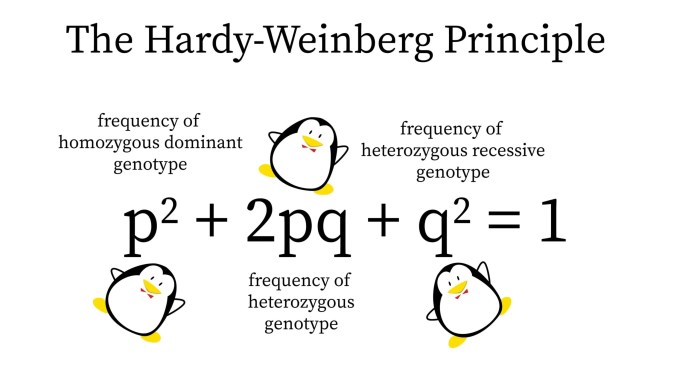
p 2+ 2pq + q 2= 1
where:
- p is the frequency of the dominant allele
- q is the frequency of the recessive allele
- p 2is the frequency of the homozygous dominant genotype
- 2pq is the frequency of the heterozygous genotype
- q 2is the frequency of the homozygous recessive genotype
Factors Affecting Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium, Hardy weinberg equation pogil answer key
Several factors can disrupt Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, including:
- Mutation
- Gene flow
- Genetic drift
- Non-random mating
- Natural selection
These factors can alter allele and genotype frequencies, leading to deviations from the expected equilibrium.
Applications of the Hardy-Weinberg Equation
The Hardy-Weinberg equation has several applications in population genetics, including:
- Studying genetic diversity
- Understanding evolution
- Assessing conservation efforts
Limitations of the Hardy-Weinberg Equation
The Hardy-Weinberg equation is a simplified model that assumes no evolutionary influences. In reality, these influences are often present, which can limit the accuracy of the equation’s predictions.
It is important to interpret results from the equation in light of these limitations and to consider other factors that may be affecting the population’s genetic variation.
FAQ: Hardy Weinberg Equation Pogil Answer Key
What is the Hardy-Weinberg Equation?
The Hardy-Weinberg Equation is a mathematical model that describes the expected genotype frequencies in a population under certain assumptions, such as no selection, no mutation, no migration, and random mating.
What are the assumptions of the Hardy-Weinberg Equation?
The assumptions of the Hardy-Weinberg Equation are: no selection, no mutation, no migration, and random mating.
What are the limitations of the Hardy-Weinberg Equation?
The limitations of the Hardy-Weinberg Equation are that it assumes no selection, no mutation, no migration, and random mating, which are often not met in real populations.