Discover the comprehensive soil texture worksheet answer key pdf, an indispensable resource for understanding the fundamental principles of soil texture classification. This guide empowers readers with the knowledge and tools to analyze and interpret soil texture, unlocking a deeper comprehension of soil properties and their impact on plant growth and agricultural practices.
Delving into the intricacies of soil texture, this worksheet provides a systematic approach to classifying soil types based on their particle size distribution. It unravels the mysteries of soil texture triangles, enabling users to determine soil texture class with precision.
Furthermore, the worksheet explores the profound relationship between soil texture and plant growth, highlighting the critical role of soil texture in water retention, nutrient availability, and root development.
Soil Texture Classification
The United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) soil texture classification system is a widely used method for classifying soils based on their particle size distribution. This system divides soil particles into three main categories: sand, silt, and clay.
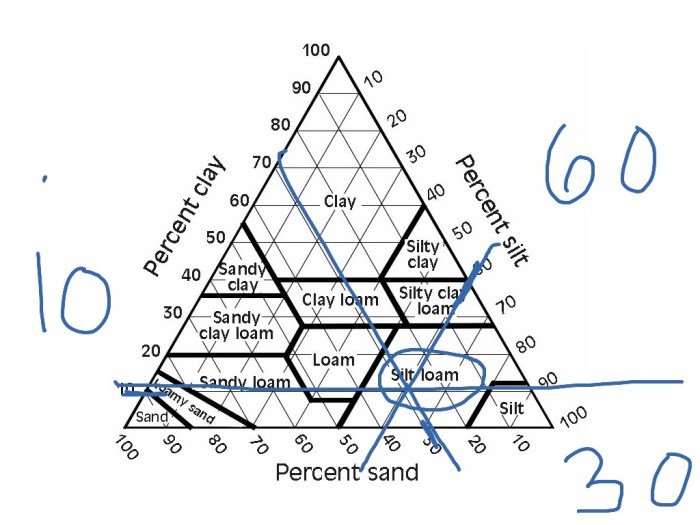
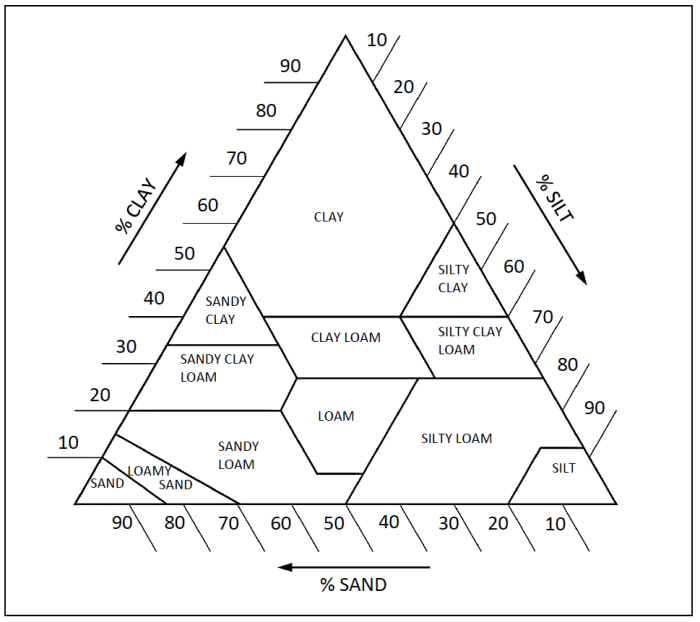
The USDA soil texture triangle is a graphical representation of the USDA soil texture classification system. It is a triangular diagram that shows the percentage of sand, silt, and clay in a soil sample. The triangle is divided into 12 soil texture classes, ranging from sand to clay.
Soil Texture Classes, Soil texture worksheet answer key pdf
| Soil Texture Class | Sand (%) | Silt (%) | Clay (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sand | >90 | <10 | <10 |
| Loamy sand | 80-90 | 10-20 | <10 |
| Sandy loam | 70-80 | 20-30 | <10 |
| Loam | 40-70 | 20-40 | <20 |
| Silt loam | 20-50 | 50-80 | <20 |
| Silty clay loam | 20-50 | 30-50 | 20-30 |
| Clay loam | 20-40 | 20-40 | 20-40 |
| Sandy clay loam | 40-60 | 20-30 | 20-30 |
| Silty clay | <20 | 40-60 | 20-40 |
| Clay | <40 | <40 | >40 |
Soil Texture Analysis Methods
There are several methods that can be used to analyze soil texture. The most common methods are the hydrometer method and the pipette method.
Hydrometer Method
The hydrometer method is a simple and inexpensive method for analyzing soil texture. It is based on the principle that soil particles of different sizes settle at different rates in water.
- A soil sample is dispersed in water and a hydrometer is used to measure the specific gravity of the suspension at different time intervals.
- The particle size distribution of the soil sample is then calculated using a calibration curve.
Pipette Method
The pipette method is a more accurate method for analyzing soil texture than the hydrometer method. It is based on the principle that soil particles of different sizes settle at different rates in water.
- A soil sample is dispersed in water and a pipette is used to withdraw a sample of the suspension at a specific depth and time.
- The particle size distribution of the soil sample is then calculated using a calibration curve.
Soil Texture Triangle: Soil Texture Worksheet Answer Key Pdf
The soil texture triangle is a graphical representation of the USDA soil texture classification system. It is a triangular diagram that shows the percentage of sand, silt, and clay in a soil sample. The triangle is divided into 12 soil texture classes, ranging from sand to clay.
The soil texture triangle can be used to determine the soil texture class of a soil sample by plotting the percentage of sand, silt, and clay on the triangle.
Interactive Soil Texture Triangle
| Sand (%) | Silt (%) | Clay (%) |
|---|---|---|
Soil Texture and Plant Growth
Soil texture has a significant impact on plant growth. The texture of a soil affects its water holding capacity, nutrient availability, and root development.
Water Holding Capacity
Sandy soils have a low water holding capacity because they have large pores that allow water to drain quickly. Clay soils have a high water holding capacity because they have small pores that hold water tightly.
Nutrient Availability
Sandy soils are often low in nutrients because they have a low cation exchange capacity. Clay soils are often high in nutrients because they have a high cation exchange capacity.
Root Development
Sandy soils are easy for roots to penetrate, but they provide little support for roots. Clay soils are difficult for roots to penetrate, but they provide good support for roots.
Matching Soil Texture to Plant Species
It is important to match the soil texture to the specific plant species that you are growing. Some plants, such as tomatoes, prefer sandy soils. Other plants, such as corn, prefer clay soils.
Soil Texture Management Practices
There are several management practices that can be used to improve soil texture. These practices include:
Adding Organic Matter
Adding organic matter to the soil can improve soil structure and water infiltration. Organic matter can also help to increase the cation exchange capacity of the soil, which makes nutrients more available to plants.
Managing Soil Compaction
Soil compaction can occur when the soil is subjected to excessive pressure. Compacted soils have a reduced water infiltration rate and are more difficult for roots to penetrate. Soil compaction can be managed by reducing the amount of traffic on the soil and by using cover crops.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of a soil texture worksheet?
A soil texture worksheet provides a structured approach to analyzing and classifying soil based on its particle size distribution, enabling users to determine soil texture class.
How does soil texture affect plant growth?
Soil texture plays a crucial role in plant growth by influencing water holding capacity, nutrient availability, and root development. Different soil textures can have significant implications for crop production and agricultural practices.