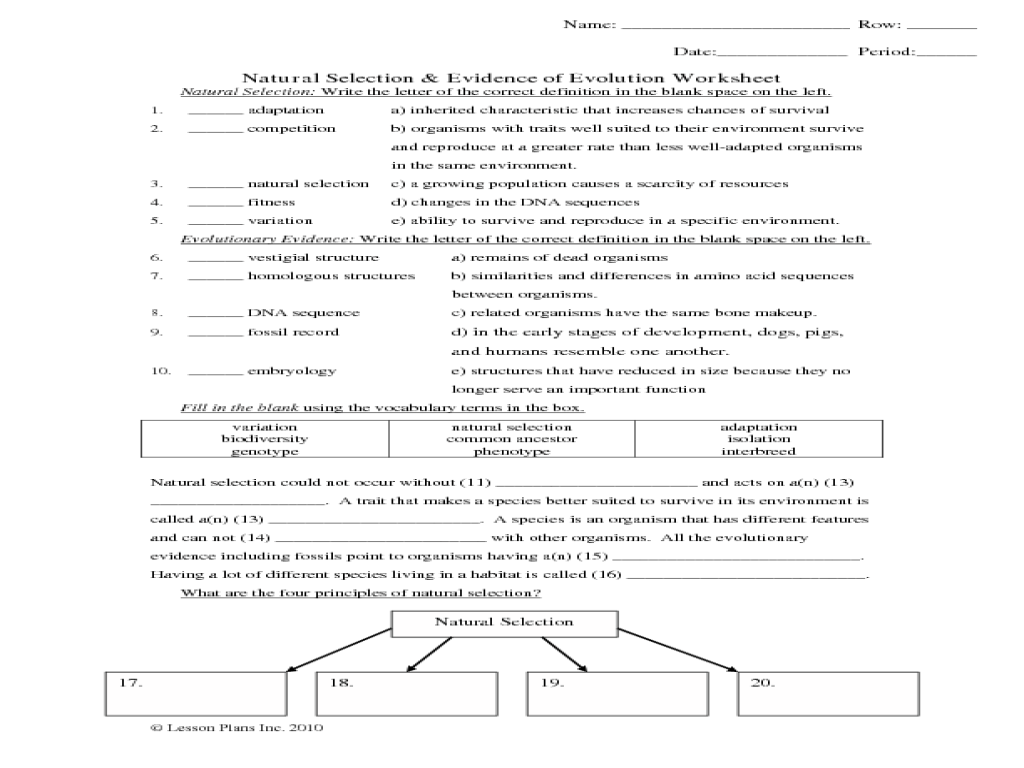
Evolution by natural selection worksheet answers provide a deeper understanding of the mechanisms and processes that drive evolutionary change. These answers shed light on the evidence supporting the theory of evolution and its applications across various fields, including medicine, agriculture, and conservation biology.
Delving into the concepts of genetic variation, natural selection, and genetic drift, these answers unravel the intricacies of evolution. They explore the fossil record, comparative anatomy, and patterns of speciation, demonstrating the interconnectedness of life on Earth.
1. Introduction
Evolution by natural selection is a fundamental concept in biology that explains how species change over time. This theory, proposed by Charles Darwin, states that individuals with traits that make them better adapted to their environment are more likely to survive and reproduce, passing on their advantageous traits to their offspring.
Over many generations, this process leads to the gradual evolution of species.
The worksheet answers provide a comprehensive overview of the key concepts and evidence supporting the theory of evolution by natural selection.
2. Evidence of Evolution
Fossil Record
The fossil record provides direct evidence of the evolution of species over time. Fossils are the preserved remains or traces of ancient organisms. By studying fossils, scientists can observe the changes in the morphology, behavior, and distribution of species over millions of years.
Comparative Anatomy
Comparative anatomy involves comparing the anatomical structures of different organisms. Homologous structures are structures that have similar form and developmental origin in different species, indicating a shared ancestry. Analogous structures, on the other hand, are structures that serve similar functions but have different origins, reflecting adaptations to similar environmental pressures.
3. Mechanisms of Evolution
Genetic Variation, Evolution by natural selection worksheet answers
Genetic variation is the raw material for evolution. It arises from mutations, genetic recombination during meiosis, and gene flow between populations. Genetic variation provides the diversity of traits upon which natural selection can act.
Natural Selection
Natural selection is the driving force of evolution. It favors individuals with traits that enhance their survival and reproductive success in a given environment. Over time, this leads to the accumulation of advantageous traits in a population.
Genetic Drift
Genetic drift is a random change in the allele frequencies of a population, particularly in small populations. It can lead to the loss of genetic variation and the fixation of alleles, potentially driving evolutionary change.
4. Patterns of Evolution: Evolution By Natural Selection Worksheet Answers
Speciation
Speciation is the process by which new species arise. It occurs when populations of a species become reproductively isolated from each other, leading to the accumulation of genetic differences and the eventual formation of new species.
Types of Speciation
- Allopatric speciation: Populations are separated by a geographic barrier.
- Sympatric speciation: Populations diverge within the same geographic area.
- Parapatric speciation: Populations diverge along an environmental gradient.
5. Applications of Evolutionary Theory

Medicine
Evolutionary theory has revolutionized medicine. It provides insights into the genetic basis of diseases, the development of drug resistance, and the evolution of pathogens. This knowledge aids in the design of effective treatments and preventive measures.
Agriculture
Evolutionary theory is essential for agricultural practices. It guides the development of new crop varieties and livestock breeds with desirable traits, such as increased yield, disease resistance, and adaptability to changing environmental conditions.
Conservation Biology
Evolutionary theory informs conservation strategies. It helps identify endangered species, understand their evolutionary history, and predict their vulnerability to environmental changes. This knowledge supports efforts to preserve biodiversity and protect ecosystems.
Q&A
What is the central concept of evolution by natural selection?
Natural selection is the driving force of evolution, favoring individuals with advantageous traits that enhance their survival and reproductive success.
How does the fossil record support the theory of evolution?
The fossil record provides a chronological sequence of organisms, demonstrating the gradual changes in species over time, supporting the concept of descent with modification.
What is the difference between homologous and analogous structures?
Homologous structures share a common ancestry, while analogous structures perform similar functions but have different evolutionary origins.